Area-averaged Temperatures, Precipitation and the
Growing Season & Vegetation Period in
Maryland: 1 January - 31 December, 2024
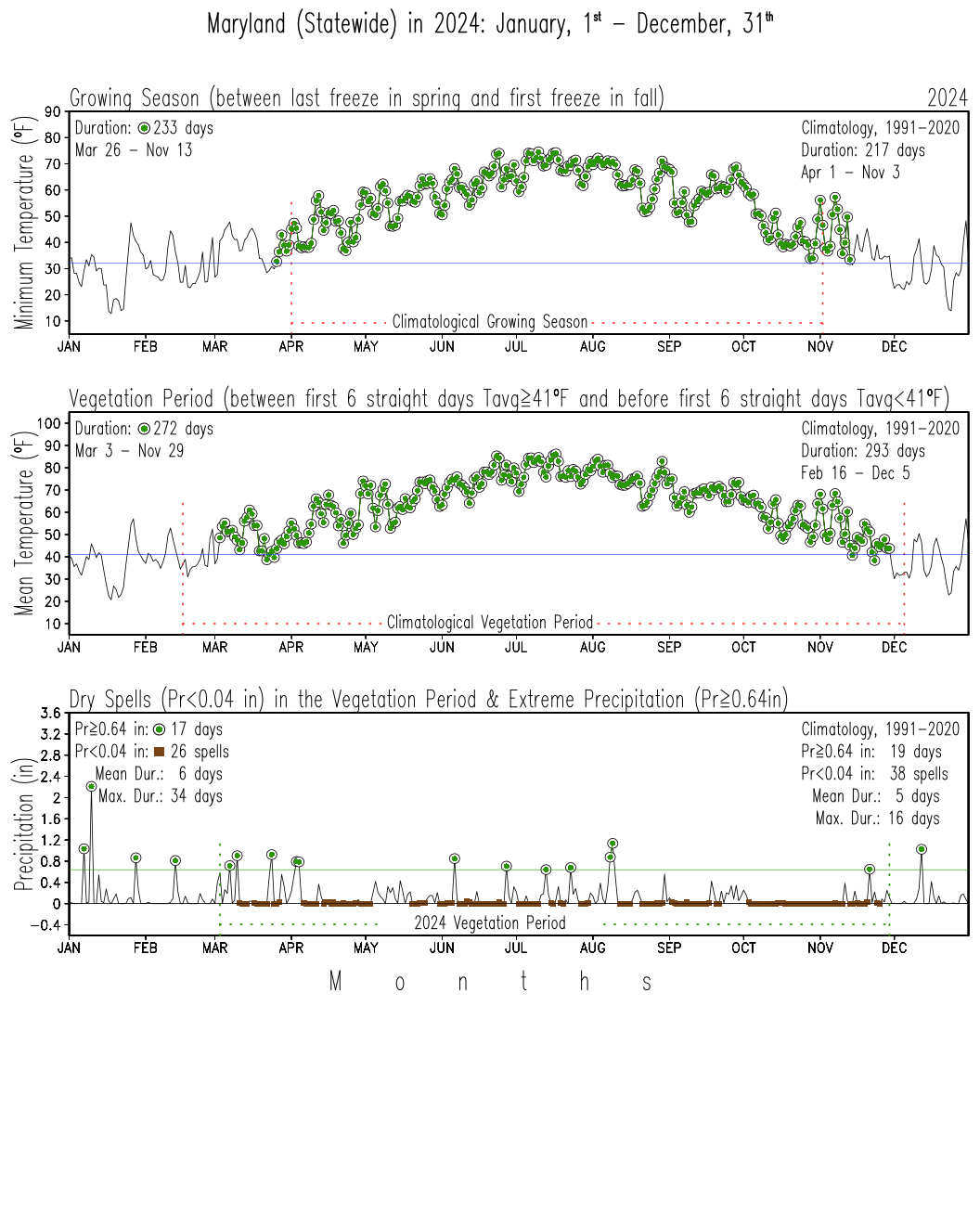
This analysis obtains the Growing Season and the Vegetation Period for the calendar year from area-averaged daily temperatures. The Growing Season is defined as the period between the day after the last frost of spring and the day before the first frost of fall when the minimum air temperature is above the freezing point of 32°F (USEPA, 2023). Thus, the growing season focuses on the weather conditions that allow crops and plants to grow actively (e.g., Körner et al., 2023).
The Vegetation Period is defined as the period between the first day of the first occurrence of a 6-day period with daily mean temperatures equal to or above 41°F and the day before the first occurrence of a 6-day period with daily mean temperatures below 41°F after the first of July (Tschurr et al., 2020). Hence, the vegetation period captures weather conditions that allow plants to grow at a different pace, even if it is minimal; the vegetation period, in this way, can last the whole year, including the dormant period. The number of dry spells is particularly important during the vegetation period (Tschurr et al., 2020).
The duration of the growing season, the vegetation period, and the longest dry spell within the vegetation period can be used as climate change indicators to track how conditions for vegetation change with time.
Summary tables can be seen in the following links for the Growing Season and the Vegetation Period for the calendar year.
NOTE: The plots are created from preliminary NCEI's nClimDiv-Daily data set, v1.0.0. Data labeled as scaled on January 10, 2025.